Ww1 German Biplane - The Fokker Dr.I (Dreidekker, "tripleon" in German), often known simply as the Fokker Triplane, was a World War I fighter aircraft designed by Fokker-Flyzigorki. Dr. Moon rendered great services in the spring of 1918. She became famous as the aircraft in which Manfred von Richthof achieved his last 17 victories (in addition to his previous two in the prototype Fokker F.I in September 1917) and in which he was killed. April 21, 1918.
Despite her unique Vickers machine gun armament, Sweptwith quickly proved superior to the more heavily armed Albatross fighters used by liftstraat ships.
Ww1 German Biplane
In April 1917, Anthony Fokker visited Justa 11 and saw a captured Sopwith triplane. Upon his return to the Schwerin factory, Fokker commissioned Reinhold Platz to build the triplane, but did not give him much information on the Sopweth's design.
Amazon.com: Nyair Hang Retro Airplane Aircraft Model, Retro World War I German Wings Model,ww1 Aircraft Model For Bar, Desktop Or Home Decor Decoration (yellow)
Platz responded with the V.4, a small rotary triplane with a steel-tube fuselage and thin cantilever wings.
It was first developed during the collaboration between the government of Fokker and Hugo Junkers. Early tests revealed that the V.4 had unacceptably high control forces, resulting from the use of unbalanced ailerons and elevators.
Instead of putting the V.4 through a type test, Fokker produced a revised prototype designated the V.5. The most notable changes were the introduction of horn-balanced ailerons and elevators, as well as the introduction of long span wings. The V.5 also featured interplanetary struts, which were unnecessary from a structural point of view, but which reduced the flexibility of the wing.
On 14 July 1917 Idflieg placed an order for 20 pre-production aircraft. Prototype V.5, serial 101/17, was tested for destruction at Adlershof on 11 August 1917.
German Metal Henschel Wwi Wwii Airplane Biplane Bomber
The first two pre-production triplanes were designated FI, after the initial class prefix of Idflieg. These aircraft, serial numbers 102/17 and 103/17, were the only machines to receive the F.I designation.
And the leading edge of the tailplane can be separated from the next plane by a slight convex curve. Both ships arrived at Markbeck, Belgium on 28 August 1917, for combat overhauls on the 10th and 11th.
Richthof flew 102/17 on 1 September 1917 and shot down two Ammi aircraft over the next two days. He told the Kogluft (Kommandierder Geral der Luftstreitkräfte) that the F.I was superior to the Sopwith Triplane.

Combat study came to an abrupt halt, with Oberleutnant Kurt Wolff, Staffelführer of Jasta 11, shot down 15 September 102/17, and Leutnant Werner Voss, Staffelführer of Jasta 10, killed 102/17 September.
Wwi Albatros D V German Biplane Fighter (profi Pack Plastic Kit) 1/48 Eduard
Idflieg placed a production order for 100 tonnes of the aircraft in September, followed by an order for 200 in November.
Except for the straight edge of the tailplane, these aircraft were nearly identical to the F.I. The main distinguishing feature was the addition of wing skids, which proved necessary because the aircraft was prone to landing difficulties and ground looping.
Compared to the Albatros and Pfalz fighters, the Dr. I offered unusual maneuverability. While the ailerons weren't very effective, the rudder and elevator controls were light and powerful.
Weissfeld Weibel Franz Hammer Jasta 6 said: "The triplane was my favorite fighting machine because it had such wonderful flying qualities that I could afford to do stunts - looping and rolling - and dive with complete safety." . Give up because even though he was very smart, he wasn't faster.
Did German Armored Aircraft Invent \
As Hammer noted, Doctor I was much slower in level flight and dope than contemporary Allied fighters. While the initial rate of climb was excellent, performance was drastically reduced at high altitudes due to the low compression of the Obersal Ur.II, a clone of the Le Ron 9J rotary engine.
As the war continued, chronic shortages of castor oil made rotational operations extremely difficult. The poor quality of German substitute lubricants caused many engines to fail, especially during the summer of 1918.
Furthermore, the proximity of the gunwale to the cockpit, coupled with inadequate shock padding, made the pilot vulnerable to serious head injury following a crash landing.

On 29 October 1917, Leutnant der Reserve Heinrich Guntermann, Staffelführer of Justa 15, was performing aerobatics when his plane crashed.
Fokker Triplane Dr 1 Ww1 Fighter Plane In German Markings Displaying At Duxford Airshow Stock Photo
Gunterman Song was killed in the crash landing. Leutnant der Reserve Günther Pastor of Jasta 11 was killed two days later when his triplane crashed in level flight.
Examination of the wreck revealed that the wings were of poor construction. Tests of other top-level fullbacks confirmed these results. On 2 November, Idflieg grounded all remaining fullbacks for inquiry. Idflieg conducted a Sturzkommission (accident commission) which concluded that poor construction and lack of waterproofing had allowed moisture to damage the wing structure.
In response to the crash investigation, Fokker was forced to improve quality control on the production line, especially the painting of the spars and wing ribs, to combat the moisture. Fokker also strengthened the rubber frame and attached the rubber to the auxiliary spar.
After testing the modified wing at Adlershof, Idflieg authorized the return of the triplane on 28 November 1917.
Se 5a Single Post Biplane Ww1 Aircraft Figure Fabric Posters On The Wall Picture Home Art Living Room Decoration Kh808
Production resumed in early December. By January 1918, Justis 6 and 11 were fully manned with triplanes. Only 14 squadrons used the Doctor I as primary equipment. Most of these units were part of Jagdgeschwadern I, II or III.
Despite the corrective measures, Dr. IG Wing continued to suffer from failures. On 3 February 1918, Lieutenant Hans Joachim Wolff of Justa 11 landed successfully after suffering an upper wing leading edge and rib failure.
On 18 March 1918, Luther von Richthof, Staffelführer of Justa 11, Sopwith Camels of No. 73 and Bristol F.

Postwar research showed that poor performance was not the only reason for the triplane's structural failure. In 1929, research by the National Advisory Committee on Aeronautics (NACA) found that the upper wing had a higher coefficient of lift than the lower wing: at high speeds it could be 2.55 times higher.
Ww1 Bi Plane
The Doctor I was withdrawn from front line service as the Fokker D.VII was largely withdrawn from service in June and July. Jasta 19 was the last squadron to be fully equipped with Doctor Eye.
The surviving triplanes were distributed to training and home defense units. Several trainer aircraft were equipped with the 75 kW (100 hp) Goebel Goe.II.
At the time of the armistice, many surviving triplanes were assigned to fighter training schools in Nevilles, Belgium, and Valcanes, France.
Many doctors have been used as testing grounds for experimental genes. One aircraft, designated V.7, was the Sims-Halsky Sh. III installed with Bio-Rotary Gene.
Albatros Dii Imperial Germany Army Service Wwi By Postage Stamp Models Ps5405 1 Scale 1:70 Eztoys
Serial 108/17 was used to test the 118 kW (160 hp) Goebel Goe. III, while the 469/17 series was used to test the 108 kW (145 hp) Oberursel Ur. III.
None of these genes were used productively. A triplane was used as a testbed for an experimental gear-driven Schwade supercharger.
Three ships are known to have survived the armistice. Serial 528/17 was kept as a test bed at the Deutsch Versuchsanstalt für Luftfahrt (German Aviation Research Institute) in Adlershof. After being used in the filming of two films, 528/17 is believed to have been an accident from the late 1930s.
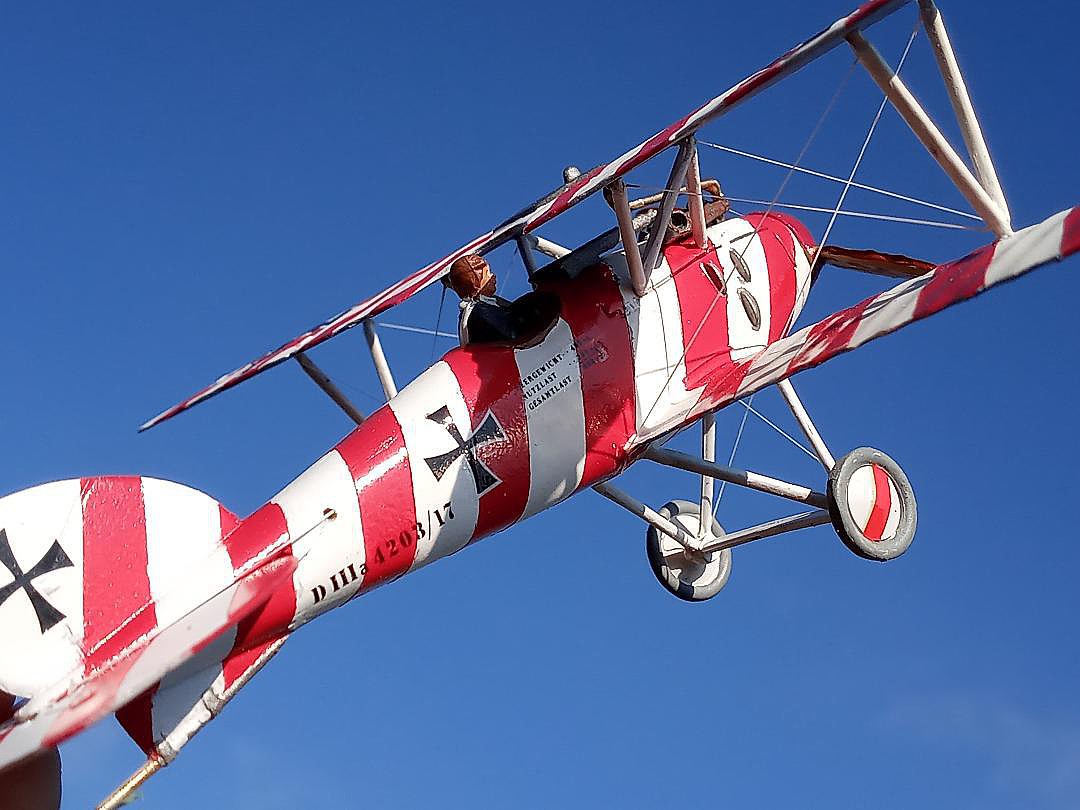

The 152/17 series, in which Manfred von Richthof scored three victories, is on display in the Zeughaus Museum in Berlin.
German Ww1 Biplane
In 1932, Fokker assembled one of the current components, the Dr. I. It was shown at the Deutsche Luftfahrt-Sammlung in Berlin. In 1943, the aircraft was destroyed in an Allied bombing raid. Only a few original Dr. I artifacts remain in the museum today.
A large number of replica and reproduction aircraft have been built for the public and for museums. Bitz Flugzeugbau GmbH produced two replicas of the Dr.I, serial numbers 001 and 002, for use in the 1966 Twentieth Century Fox film The Blue Max. Replica 001 is the oldest surviving example of the EI-APW Dr.1 . Due to the availability and scarcity of genuine rotary engines, most airworthy replicas include the Warner Scrubber or Continental R-670 radial engine. Fokker D.VII reproduction operated at NMUSAF. The aircraft is painted in the colors of Leutnant Rudolf Stark of Jasta 35b
The Fokker D.VII was a German World War I fighter designed by Reinhold Platz of Fokker-Flyzigorek. Germany produced approximately 3,300 D.VII aircraft in the second half of 1918. In service with the Luftstreitkräfte, the D.VII quickly proved to be a powerful aircraft. War was specifically called for, as the fourth clause of the "Provisions relating to the Western Front" required Germany to hand over all D.VIIs to the Allies.
Fokker's chief designer, Reinhold Platz, had been working on a number of V-series experimental aircraft since 1916. The aircraft were notable for their use of cantilever wings. Hugo Junkers and his aviation company pioneered the idea in 1915 with the first practical all-metal aircraft, the Junkers 1 monoplane, called the Blechesel (Sheet Metal Donkey or Tin Donkey). The leaves were thin, with a rounded front edge. The wing's airfoil shape provided more lift, with its relatively "blunted" leading edge (as in cross-section C) giving it more aggressive stall behavior than thinner wings commonly used.
An Inside Look At The Germans' Deadly Bomber
At the end of 1917, Fokker built the V 11 experimental biplane, equipped with the standard Mercedes D.IIIa engine. In January 1918, Idflieg held a battle competition
Fokker biplane ww1, ww1 biplane kit, rc ww1 biplane, ww1 biplane game, british biplane ww1, ww1 biplane models, ww1 biplane, lego ww1 biplane, ww1 nieuport biplane, ww1 biplane for sale, ww1 biplane plans, german biplane ww1
0 Comments